Technology has reached a stage where the boundaries between physical and digital experiences are blurring. Extended Reality (XR) is a term that encompasses this transformative change. From immersive games and virtual training to enhanced remote collaboration, XR is driving innovation across industries. But what exactly is XR, and why is it becoming a buzzword in tech circles? This guide breaks down everything you need to know.
What Is Extended Reality (XR)?
Extended Reality (XR) is an umbrella term that covers all immersive technologies- namely Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR). These technologies combine the physical and digital worlds to create enhanced or entirely new experiences.
Virtual Reality (VR)
VR technology creates completely artificial environments that replace users’ physical surroundings entirely. VR requires headsets like Oculus Quest or HTC Vive, offering immersive environments where users can explore 3D spaces, often for gaming, simulations, or training.
Augmented Reality (AR)
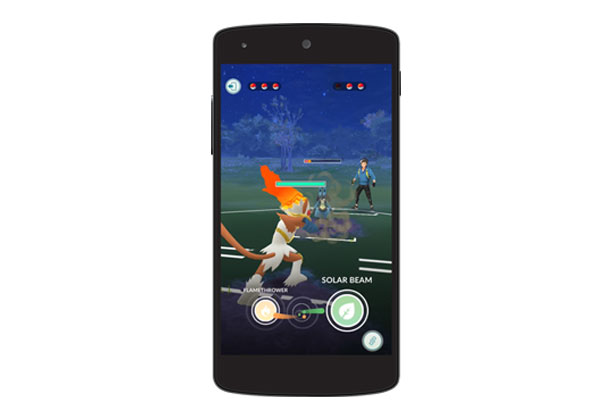
Popularized by apps like Pokémon GO and AR filters on Instagram and Snapchat, AR enhances real-world environments using smartphones or AR glasses like Microsoft HoloLens. This technology demonstrates how it can enable smartphone cameras and specialized glasses to project interactive virtual objects seamlessly onto actual surroundings.
Mixed Reality (MR)
MR blends the best of both VR and AR. It allows digital and physical objects to coexist and interact. This is highly useful in applications like remote surgery, engineering design, and collaborative workspaces. Users manipulate holographic content while maintaining awareness of their actual surroundings, creating unprecedented collaborative experiences across professional industries.

How Extended Reality works
Extended Reality (XR) functions through the seamless integration of advanced hardware, software, connectivity, and user interface technologies. Together, these components create immersive environments that blend the real and digital worlds. Here’s a detailed breakdown of how each element works:
Hardware
- Head-Mounted Displays (HMDs): These are wearable devices like Oculus Quest, HTC Vive, or Microsoft HoloLens that project virtual elements directly into the user’s field of vision. Some are tethered to computers, while others are standalone units with built-in processing power.
- Sensors & Cameras: These track the user’s physical position, motion, and environmental surroundings. Cameras help in capturing spatial data for AR/MR, while inertial measurement units (IMUs) track movement for immersive responsiveness.
- Haptic Devices: Gloves, suits, or handheld controllers provide tactile feedback, simulating touch or pressure. This enhances realism in training simulations, virtual interactions, and gaming.
- Spatial Computing Devices: These devices understand and map the physical environment in real time, allowing digital elements to interact with real-world surfaces or objects.
- Smartphones & Tablets: For many AR applications, mobile devices serve as accessible XR platforms through their screens, GPS, accelerometers, and AR-compatible chips.
Software
- XR Development Platforms: Engines like Unity and Unreal Engine are commonly used to develop XR applications. These platforms support 3D modeling, physics simulation, lighting, animation, and real-time rendering.
- XR SDKs and APIs: Software Development Kits (SDKs) such as ARKit (Apple), ARCore (Google), and Microsoft’s Mixed Reality Toolkit provide prebuilt tools and libraries to simplify XR app creation and enhance cross-platform compatibility.
- Cloud-Based XR Services: These offer scalable processing and data storage solutions, enabling real-time multiplayer experiences, streaming of heavy 3D content, and dynamic content updates without relying solely on device storage.
Connectivity
- 5G Networks: XR applications, especially in enterprise and multiplayer gaming, demand high-speed, low-latency connections. 5G enables rapid data transmission, real-time updates, and higher bandwidth for AR cloud streaming and VR telepresence.
- Edge Computing: By processing data closer to the source (i.e., near the user), edge computing reduces latency and supports real-time feedback—critical in XR applications such as remote surgeries or factory monitoring.
- Wi-Fi 6 and Beyond: Newer Wi-Fi standards enhance in-building connectivity, which is important for indoor XR experiences like museums, classrooms, and enterprise setups.
User Interfaces (UI) & Interaction Systems
- Gesture Recognition: Cameras and motion sensors detect hand gestures, allowing users to interact naturally without physical controllers. This is especially useful in MR and AR interfaces.
- Eye Tracking: Integrated sensors track eye movements to adjust focus, navigate menus, or trigger interactions. It also enhances realism by enabling foveated rendering, which focuses graphical power where the user is looking.
- Voice Commands: Natural language processing allows users to control XR environments using voice, improving accessibility and hands-free interaction.
- Haptic Feedback: From subtle vibrations to full-body suits, haptics simulate physical sensations, enriching immersion. For example, a user can “feel” the recoil of a virtual gun or the texture of a virtual object.
- Spatial Audio: Directional sound simulates how we perceive audio in real life. This makes XR environments feel more lifelike and aids navigation and situational awareness.
Industrial Applications of XR
Here are some of the most promising applications of extended reality:
Retails and Virtual Showrooms:
Imagine walking through a sleek showroom from your couch, Extended Reality lets shoppers explore products, try them virtually, and make confident purchases without stepping foot in a physical store.
Immersive Entertainment & Future of Gaming
Gaming isn’t just play, it’s a portal now. XR transports players into lifelike worlds where every move counts, turning simple gameplay into fully immersive adventures that feel like alternate realities.
Urban Development
City planners use XR to walk through future buildings before they’re built. From traffic flow to sunlight exposure, XR helps visualize and solve real problems in urban design efficiently.
Fashion, Design, and 3D Dilemma
Designers can now drape digital fabric on virtual models. XR solves the 3D fitting dilemma, letting fashion brands prototype styles faster, reduce waste, and enthuse clients with virtual runway previews.
Enterprise Application
From remote collaboration to virtual training, XR boosts workplace productivity. Teams can meet inside virtual spaces, train safely in simulations, and solve problems together, no matter where they are physically.

Benefits of Extended Reality Solutions
Enhanced Design Accuracy and Visualization
XR enables professionals to interact with 3D models at a 1:1 scale, offering a clearer understanding of spatial layouts and design elements that are hard to grasp on 2D screens.
Boosts Creativity and Real-Time Iteration
Immersive environments allow for instant feedback and design modifications, encouraging creative experimentation and reducing costly revisions during the physical production or construction phase.
Efficient Remote Collaboration
XR supports global teamwork by creating shared virtual spaces where team members can meet, review designs, and make real-time decisions without needing to travel.
Improved Training Through Realistic Simulations
Workers can safely practice complex tasks in immersive VR simulations, making training more effective while reducing risk, especially valuable in high-risk industries like manufacturing and healthcare.
Greater Workflow Efficiency
By integrating visualization, collaboration, and training into a single immersive platform, XR streamlines project timelines and improves decision-making across professional sectors.
Challenges in XR Adoption
Upfront Investment Hurdles
While XR opens doors to transformation, the cost of entry, especially high-end hardware and custom software, can be a major obstacle for smaller organizations with limited budgets.
Tech Gaps and Hardware Limitations
Laggy interactions, low-resolution visuals, and short battery life still frustrate users, showing there’s a long road ahead before XR reaches truly seamless performance.
Complex Content Demands
Building high-quality, interactive XR experiences isn’t plug-and-play. It demands skilled creators, robust tools, and time, often a deterrent for companies exploring XR for the first time.
Data Safety and Privacy Risks
With XR systems gathering environmental and behavioral data, securing user information, and ensuring ethical usage has become a top concern, especially in healthcare and corporate applications.
Fragmented Ecosystem
Too many platforms and incompatible systems mean users can’t enjoy consistent XR experiences across devices, and unified standards are still a work in progress for the industry.
Dive into the future of immersive tech with us!
Juego neXR: Powering XR Innovation
At Juego neXR, we craft cutting-edge Extended Reality (XR) solutions that transform how industries approach training and operations. Leveraging the power of XR technologies, including Virtual and Augmented Reality, we design immersive, interactive environments that bring real-world precision to virtual learning experiences.
Our solutions simulate complex, high-stakes scenarios with accuracy, enabling professionals to build confidence, sharpen skills, and respond effectively in both routine and unexpected situations, all without real-world risks.
From scalable enterprise XR simulations to tailored, high-fidelity environments, our offerings are built to boost efficiency, reduce training costs, and enhance overall safety.
Conclusion
Extended Reality is no longer just a buzzword, it’s a transformative force reshaping how we live, work, learn, and play. From the fundamentals of XR technology to its real-world applications in gaming, urban planning, retail, and professional training, XR is proving to be a cornerstone of the digital future. As both opportunities and challenges emerge, one thing is clear: extended reality solutions today will define tomorrow’s innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Extended Reality (XR) can transform your business by streamlining operations and elevating customer engagement through immersive, interactive experiences. From virtual product demos and 3D showrooms to realistic employee training simulations, XR reduces costs, boosts efficiency, and enhances decision-making. For customer engagement, XR offers memorable, hands-on digital interactions that increase satisfaction and retention.
Extended Reality (XR) enhances a wide range of training and skill development, including technical, soft, and safety-critical skills. Industries like aviation, manufacturing, and healthcare use XR for realistic simulations, from operating machinery to emergency response. Soft skills such as public speaking or customer interaction can also be improved through immersive roleplay. XR enables repeatable, risk-free practice with real-time feedback, accelerating learning outcomes.
Small businesses can adopt XR technology cost-effectively by starting with scalable solutions like mobile AR apps or affordable VR headsets. Leveraging open-source platforms such as Unity and Unreal Engine reduces development costs, while outsourcing to experienced partners like Juego neXR eliminates the need for in-house XR teams. Prioritizing pilot projects in areas like training or virtual product demos helps demonstrate ROI before full-scale deployment. Cloud-based XR tools also minimize infrastructure investment.
The future of XR lies in spatial computing, AI-integrated environments, and cross-platform interoperability. Expect more intuitive interfaces, real-time collaboration across geographies, and hyper-realistic simulations for training and design. As 5G and edge computing expand, XR experiences will become smoother and more accessible. To stay ahead, focus on scalable, adaptive XR solutions tailored to your industry.
Revolutionize the future of business with Juego neXR
Related Posts
Share this Article:
Our Offices

India
Bangalore
GR Grand Plaza, 2nd Floor, JP Nagar, 6th Phase, Bangalore – 560 078
KSA
Jeddah
St Idris Square, 4036 Helmi Koutbi, Al Zahra, Jeddah 23425, Saudi Arabia
Follow Us On:
© 2026 Juego neXR. All Rights Reserved.